5.5 Replacement and retrieve |
When you edit a large file, it's difficult to move to target position by using only cursor-move-commands and page-jump-commands. If the command which searches the character string in a text file is used, it can move to the target position quickly. There is a related substitution command, which replaces searched character string to different character string.
| Command | Action | |
|---|---|---|
| /word | Retrieve the word | |
| n | Find the next word | |
| N | Find the previous word | |
| :[line] s/AAA/BBB/[option] | Replace "AAA" to "BBB" in specific lines. Line: m,n: from m to n th lines %: every lines omission: current line Option: g: replace several word in a line |
|
Table 5-8: Search and Replace
5.5.1 Retrieve a string
In order to edit a large text quickly, we can use the command which moves cursor to the target character string.
| Format |
/word↵ |
Practice: Retrieve a string |
Open a existed file "/var/log/dmesg" using vi command.
$ vi /var/log/dmesg ↵ |
Input a string, which you want to find, after "/" command, move the string. Here, input "/CPU?" in order to find "CPU".
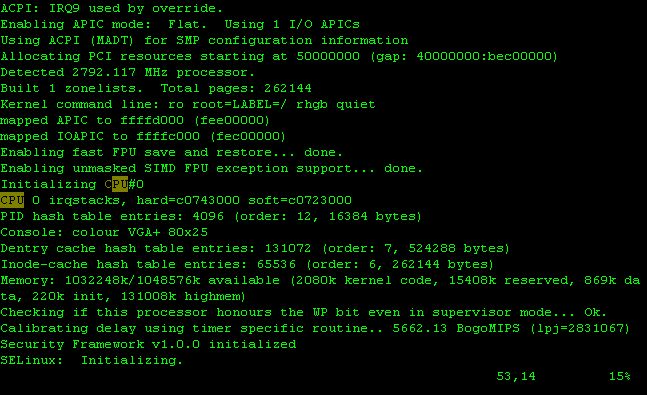
Figure 5-13: Screen
When there are the same string in a file, you can find the next string with "n" command, or the previous string with "N" command repeatedly.
Not to change the contents of the file, we use ":q!" command.
:q! ↵ |
5.5.2 Replace a string
As convenient editing function, you can replace searched character string into specified character string. The substitution is also repeatable.
| Format |
: target-line s/original-string/replace-string/option |
If target-line and option are omitted, the current line is target.
If option -g is specified, it replaces several string in the same line, otherwise it replaces only one time in each lines.
Practice: Replace a string |
Open a existed file "/var/log/dmesg" using vi command.
$ vi /var/log/dmesg ↵ |
In order to replace "CPU" to "cpu" in only a line, find "CPU" using "/CPU[Enter]" command, then replace
only that string using ":s/CPU/cpu/[Enter]" command.
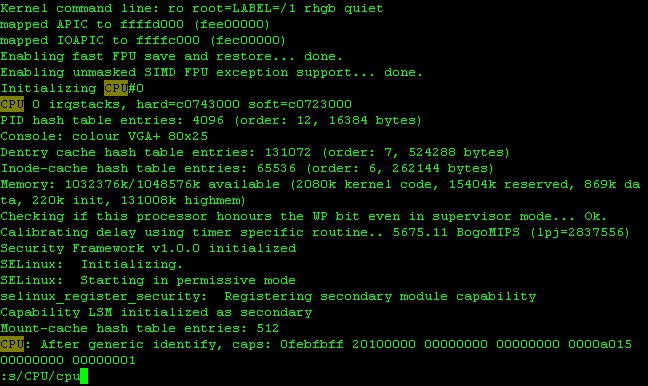
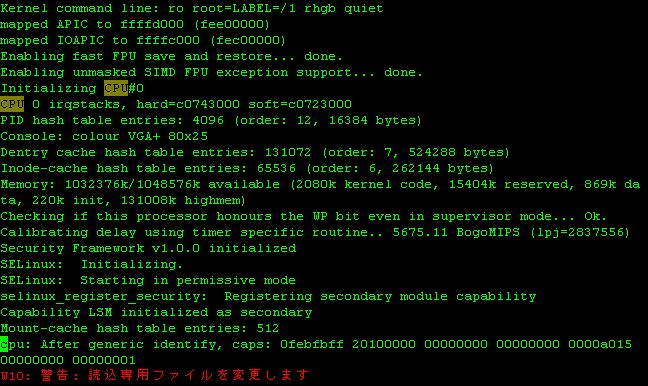
Figure 5-14: Screen
If target line is from 1 to 100 line, you can specify "1,100" as target line.
When replace in entire file, specify "%" as target line.
If you omit option, it replaces only the first found string.
The "g" option can replace every strings in the same line.
If you use "%" and "g" option, it can replace every string in a file.
Here, in order to replace every "CPU" to "cpu", input ":%s/CPU/cpu/g[Enter]" command.
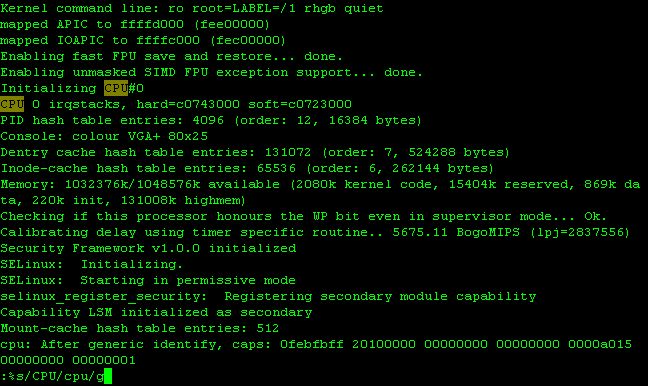
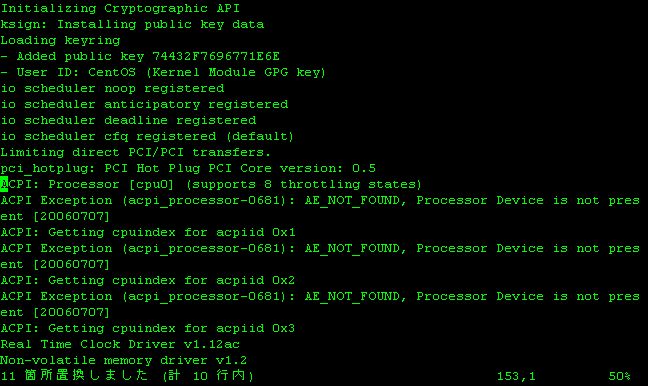
Figure 5-15: Screen 06-15a→b Before and After of Search+Replace command
Not to change the contents of the file, we use ":q!" command.
:q! ↵ |
| Command | Action | |
|---|---|---|
| /word | Retrieve the word | |
| n | Find the next word | |
| N | Find the previous word | |
| :[line] s/AAA/BBB/[option] | Replace "AAA" to "BBB" in specific lines. Line: m,n: from m to n th lines %: every lines omission: current line Option: g: replace several word in a line |
|
Table 5-9: Search and Replace
5.5.3 The easiest usage of vi command
In vi editor, you can do everything with alphabet, [Esc], [Shift], [Ctrl], and [Enter].
In both insert mode and command mode, you can use arrow keys and [BS] key.
Therefore, if you know "i" command for changing to insert mode and ":wq" command to exit with saving a
file, you can edit a file at least.
| Command | Action |
|---|---|
| [Esc] | Back to command mode |
| [Shift] | Input capital letter |
| [Ctrl] + f | Next page |
| [Ctrl] + b | Previous Page |
| ^ | Move to beginning of file in command mode |
| $ | Move to beginning of the last line in command mod |
Table 5-10: Keys used frequently
